

Kotak
Stockshaala
Chapter 1 | 3 min read
Using the FV and PV Functions for Future and Present Value Calculations
The Future Value (FV) and Present Value (PV) functions in Excel are essential tools for financial professionals, allowing for the calculation of the value of investments or cash flows at different points in time. These functions help you assess the time value of money by determining how much an investment is worth today (PV) or will be worth in the future (FV).
In this blog, we will explore how to use the FV and PV functions in Excel for financial planning and investment analysis.
What is Future Value (FV)?
Future Value (FV) represents the amount of money an investment or series of cash flows will grow over time at a given interest rate. This is especially useful for planning long-term investments like savings, retirement, or financial projects.
FV Formula in Excel: FV = PV × (1 + r)^n
Where:
- FV = Future Value
- PV = Present Value (initial investment)
- r = Interest rate per period
- n = Number of periods
Step-by-Step Guide: Using the FV Function in Excel
Example:
Suppose you invest ₹10,000 in an account that offers a 5% annual interest rate for 5 years. To calculate the future value of this investment:
1. Use the FV Function: =FV(rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type])
- rate: Interest rate per period (0.05 for 5%).
- nper: Number of periods (5 years).
- pmt: Payments made each period (0 if no periodic payments).
- pv: Present value or initial investment (-10000).
- type: Optional, when payments are due (0 for end of period).
Excel Formula: =FV(0.05, 5, 0, -10000)
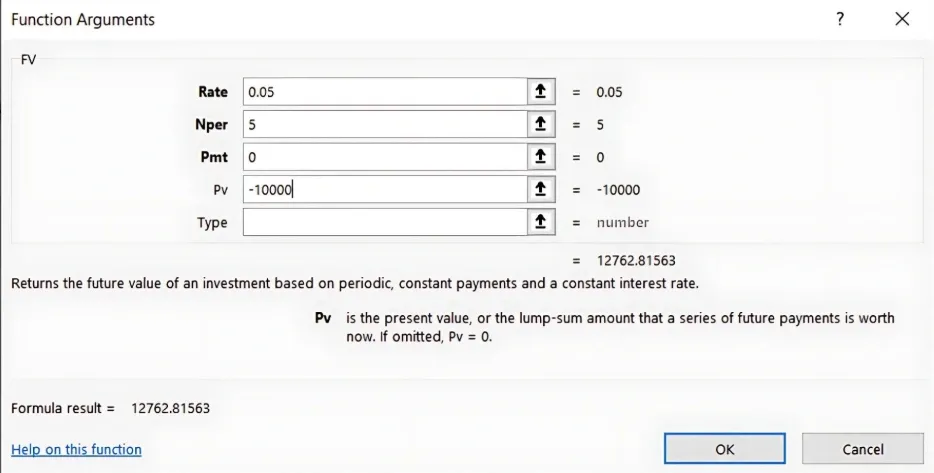
- Result: The future value of this investment would be ₹12,762.82.
What is Present Value (PV)?
Present Value (PV) represents the current value of a future sum of money or cash flows, discounted at a specific interest rate. It helps in understanding what future cash flows are worth today and is vital for investment decisions and loan calculations.
PV Formula in Excel: PV = FV / (1 + r)^n
Where:
- PV = Present Value
- FV = Future Value (expected value in the future)
- r = Interest rate per period
- n = Number of periods
Step-by-Step Guide: Using the PV Function in Excel
Example: If you expect to receive ₹15,000 five years from now and want to know its present value at a 5% interest rate:
1. Use the PV Function: =PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type])
- rate: Interest rate per period (0.05 for 5%).
- nper: Number of periods (5 years).
- pmt: Payments made each period (0 if none).
- fv: Future value (₹15,000).
Excel Formula: =-PV(0.05, 5, 0, 15000)
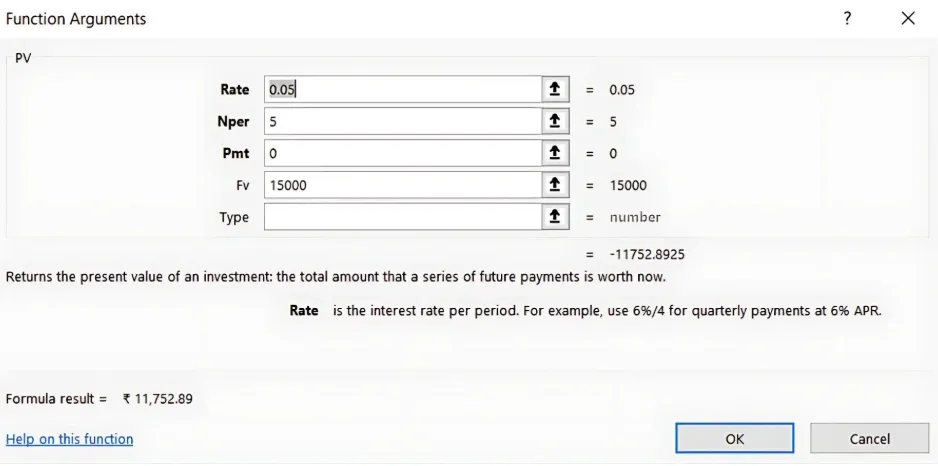
- Result: The present value of ₹15,000 received 5 years from now is ₹11,752.89 today.
Applications of FV and PV in Financial Planning
1. Investment Planning: Calculate the future value of investments based on different interest rates and time periods.
2. Loan Repayment: Use PV to determine how much a loan or mortgage is worth today and FV to project future loan balances.
3. Retirement Planning: FV can help estimate the growth of retirement savings, while PV can assess how much needs to be invested now for future goals.
Key Takeaways:
- The FV function helps project the future value of an investment based on interest rate and time.
- The PV function allows you to calculate the current value of future cash flows.
- Both functions are crucial in understanding the time value of money for financial planning and investment analysis.
Conclusion:
By mastering the FV and PV functions in Excel, you can easily project the growth of investments or determine the present value of future returns. These calculations are fundamental to making informed financial decisions, whether you're planning for retirement, evaluating investments, or managing loans.
Next Chapter Preview: In the next chapter, we’ll dive into the IRR and XIRR Functions: Calculating Returns with Variable Cash Flows, focusing on how to assess investment performance with both regular and irregular cash flows. Stay tuned to learn more about calculating returns with these advanced Excel functions!
Recommended Courses for you
Beyond Stockshaala
Discover our extensive knowledge center
Learn, Invest, and Grow with Kotak Videos
Explore our comprehensive video library that blends expert market insights with Kotak's innovative financial solutions to support your goals.














