

Kotak
Stockshaala
Chapter 3 | 2 min read
Saving for Goals: Goal-Based Financial Planning
Financial planning is more effective when tailored to specific life goals, such as buying a home, saving for a child’s education, or planning a vacation. Goal-based financial planning helps you set clear, measurable financial targets and track your progress toward achieving them. Excel is an excellent tool for organising, calculating, and tracking these goals.
In this chapter, we’ll guide you through using Excel to create a structured, goal-based financial plan.
Why Use Goal-Based Financial Planning?
-
Clarity: Define specific goals (e.g., retirement, education) and understand how much you need to save for each.
-
Tracking: Keep track of savings progress, investment returns, and timelines for each goal.
-
Adjustments: Easily update the plan as circumstances change or goals evolve.
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Financial Goals in Excel
Step 1: Define Your Financial Goals
List all your financial goals, the estimated amount needed for each, and the time horizon (years to achieve the goal). For example:
Buy a House | ₹200,000 | 10 years |
Child’s Education | ₹100,000 | 15 years |
Vacation Fund | ₹10,000 | 2 years |
Step 2: Adjust for Inflation
If the goal is long-term, consider how inflation will affect the amount you need to save. Use the FV (Future Value) function to calculate how much you’ll need in the future. Assume an inflation rate of 3%.
For example, to calculate how much you’ll need for a house in 10 years: =FV(3%, 10, 0, -200000)
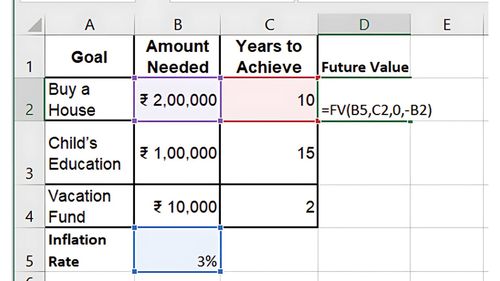
Result: You’ll need approximately ₹268,783 to buy a house in 10 years.
Step 3: Calculate Monthly Savings Required
Use the PMT function to determine how much you need to save each month to reach your goals. Assume you expect an investment return of 7%.
For the house goal: =PMT(7%/12, 10*12, 0, -268783)
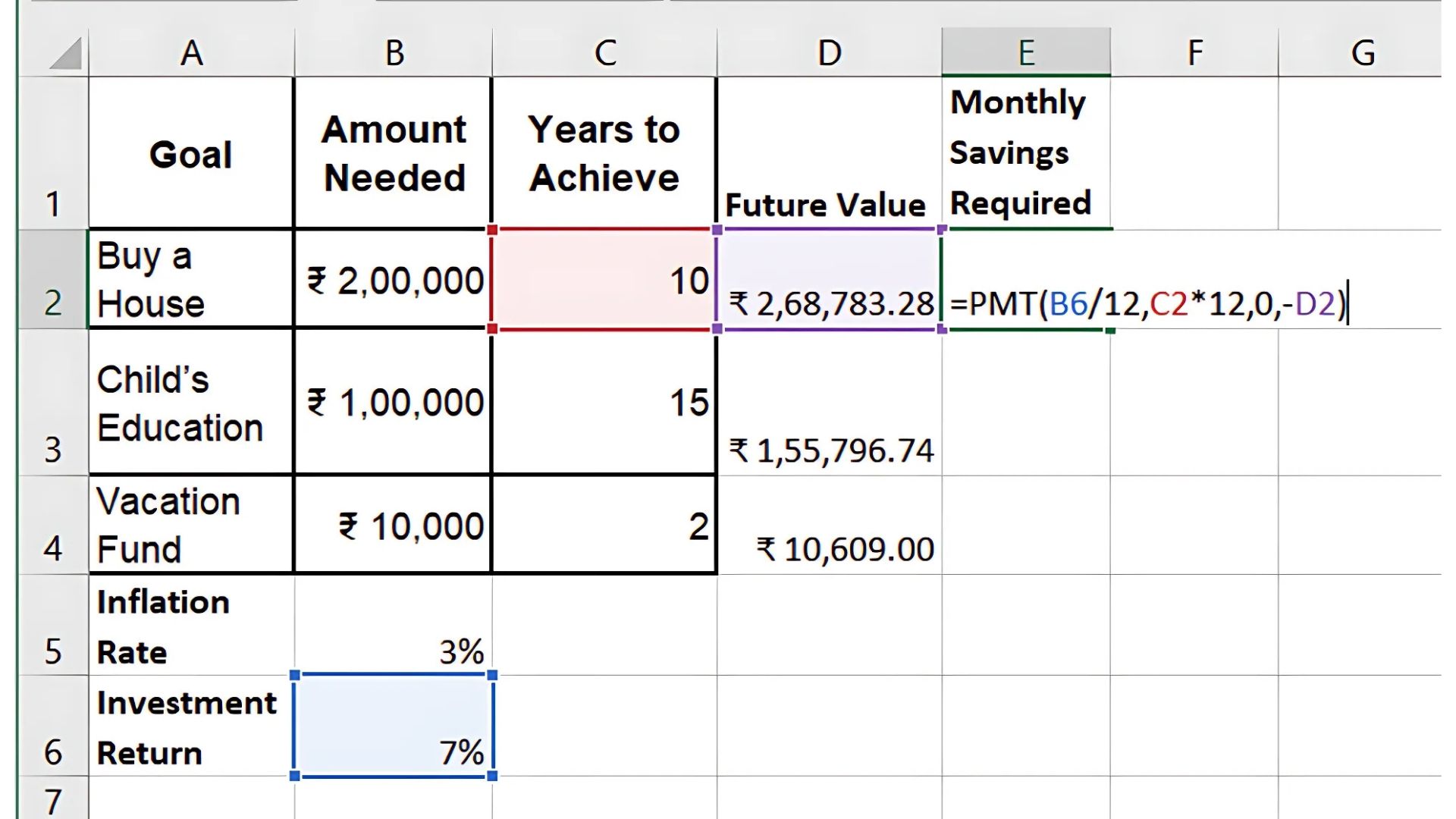
Result: You’ll need to save ₹1,552.90 monthly for 10 years to reach the goal.
Step 4: Track Progress
Create an Excel table to track the progress of your savings for each goal. Update it regularly to see how close you are to achieving your goals.
Buy a House | ₹50,000 | ₹268,783 | 18.6% |
Child’s Education | ₹20,000 | ₹155,797 | 12.8% |
Vacation Fund | ₹2,000 | ₹10,618 | 18.8% |
Step 5: Adjust Contributions as Needed
Adjust your monthly contributions if you’re falling behind on a goal or circumstances change. Excel makes it easy to recalculate using the PMT function.
Key Takeaways:
-
Goal-based planning focuses on specific financial objectives, such as buying a house or saving for education.
-
Use the FV and PMT functions in Excel to estimate how much you need to save and calculate monthly contributions.
-
Regularly update your Excel tracker to stay on top of your financial goals.
Conclusion:
Goal-based financial planning in Excel gives you a structured approach to saving for life’s important milestones. By defining clear goals, adjusting for inflation, and tracking your progress, you can stay on top of your financial future and make informed decisions.
Next Chapter Preview: In the next chapter, we’ll cover Calculating Home Loan Affordability: EMI, Interest Rate, and Tenure Impact, where you’ll learn how to determine how much home you can afford by calculating your monthly loan payments (EMI), understanding the impact of interest rates, and optimising loan tenure. Stay tuned for practical insights into home loan planning!
Recommended Courses for you
Beyond Stockshaala
Discover our extensive knowledge center
Learn, Invest, and Grow with Kotak Videos
Explore our comprehensive video library that blends expert market insights with Kotak's innovative financial solutions to support your goals.














