

Kotak
Stockshaala
Chapter 4 | 2 min read
Calculating Home Loan Affordability: EMI, Interest Rate, and Tenure Impact
Buying a home is often the biggest financial commitment you’ll make, and determining how much you can afford requires careful planning. Three critical factors impact home loan affordability: EMI (Equated Monthly Instalment), the interest rate, and the loan tenure. In this chapter, we’ll explore how to calculate these factors using Excel so you can determine what works best for your financial situation.
What is EMI?
EMI (Equated Monthly Instalment) is the fixed monthly payment made toward repaying a home loan, consisting of both principal and interest. EMI helps spread the repayment over a specified period.
EMI Formula: EMI = (P × r × (1 + r)^n) / ((1 + r)^n - 1)
Where:
-
P = Loan amount (principal)
-
r = Monthly interest rate (annual rate / 12)
-
n = Loan tenure in months
Step-by-Step Guide: Calculating EMI in Excel
Step 1: Set Up the Loan Details
For example, let’s consider:
- Loan amount = ₹500,000
- Annual interest rate = 5%
- Loan tenure = 30 years
Step 2: Use Excel’s PMT Function to Calculate EMI
The PMT function in Excel calculates the EMI. The syntax is:
=PMT(rate, nper, pv)
For this example:
=PMT(5%/12, 30*12, -500000)
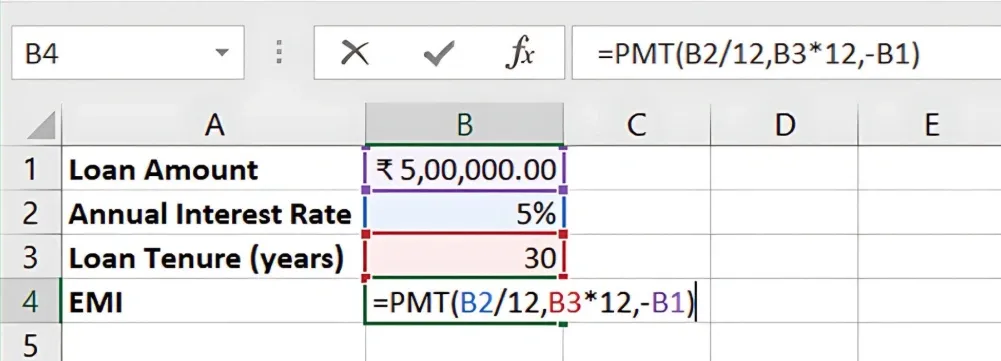
Result: The EMI for this loan is **₹2,684.11 **per month.
Step 3: Analysing the Impact of Interest Rate Changes
Interest rates can significantly affect EMI. Suppose the interest rate increases to 6%. Recalculate using:
=PMT(6%/12, 30*12, -500000)
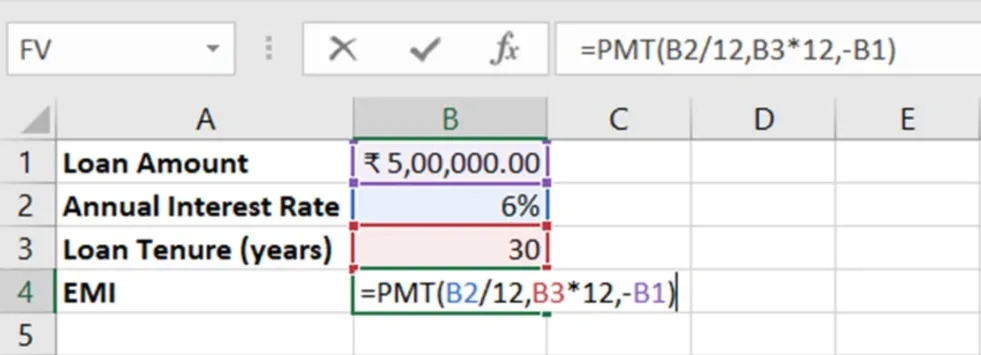
Result: The EMI increases to ₹2,997.75 per month.
This demonstrates how even a small change in interest rates can impact monthly affordability.
Step 4: Analysing the Impact of Loan Tenure
Loan tenure affects how long you’ll be paying the loan and how much total interest you’ll pay. If you reduce the tenure to 20 years:
=PMT(5%/12, 20*12, -500000)
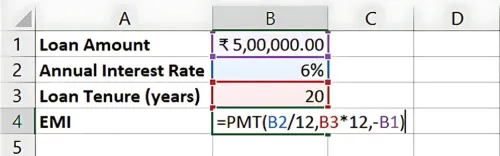
Result: The EMI for a 20-year loan is ₹3,582.16 per month, but the total interest paid will be significantly lower compared to a 30-year tenure.
Creating a Loan Affordability Model in Excel
To make informed decisions, create a table to model different loan amounts, interest rates, and tenures. Here’s an example:
₹500,000 | 5% | 30 | ₹2,684.11 |
₹500,000 | 6% | 30 | ₹2,997.75 |
₹500,000 | 5% | 20 | ₹3,299.77 |
Key Takeaways:
-
EMI is determined by the loan amount, interest rate, and tenure.
-
A higher interest rate increases EMI, and a longer tenure lowers monthly payments but increases total interest.
-
Excel’s PMT function simplifies the calculation of EMI, helping you assess home loan affordability.
Conclusion:
Home loan affordability is determined by balancing the loan amount, interest rate, and tenure. Using Excel to model different scenarios helps you make informed decisions about how much home you can afford.
Next Chapter Preview: In the next chapter, we’ll explore Building a 3-Statement Financial Model in Excel (Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow), focusing on how to create an integrated financial model to assess a company’s financial performance. Stay tuned for a comprehensive guide on financial modelling in Excel!
Recommended Courses for you
Beyond Stockshaala
Discover our extensive knowledge center
Learn, Invest, and Grow with Kotak Videos
Explore our comprehensive video library that blends expert market insights with Kotak's innovative financial solutions to support your goals.














