

Kotak
Stockshaala
Chapter 4 | 3 min read
Duration and Convexity of Bonds: Measuring Interest Rate Risk
Duration and Convexity are critical metrics for assessing the sensitivity of bond prices to changes in interest rates. Duration estimates the percentage change in a bond’s price for a 1% change in interest rates, while convexity accounts for the curvature in price change, offering a more accurate measure of interest rate risk, especially for large rate movements. These tools help investors understand and manage the impact of rate fluctuations on bond portfolios.
Why Measure Duration and Convexity?
-
Interest Rate Sensitivity: Evaluate how much bond prices might change with interest rate shifts.
-
Risk Management: Identify and manage exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
-
Bond Comparisons: Compare bonds based on their price sensitivity to rate changes.
Duration Calculation
Duration serves as an approximation of bond price sensitivity. Commonly used measures include Macaulay Duration and Modified Duration.
Modified Duration Formula:
Modified Duration = Macaulay Duration / (1 + YTM / Number of Compounding Periods per Year)
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Duration in Excel
Suppose a bond has:
- Maturity = 5 years
- Yield to Maturity (YTM) = 4%
- Annual coupon payments with a 6% coupon rate
Coupon Rate | 6% |
YTM | 4% |
Maturity | 5 years |
Step 1: Calculate the Present Value of Cash Flows
- Calculate each year’s coupon payment and face value.
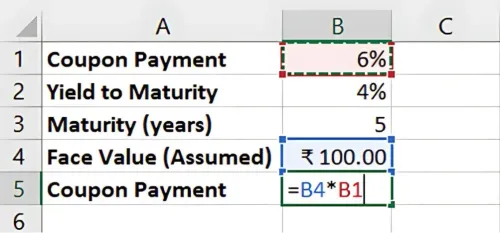
- Discount each cash flow by calculating the discount factor in Excel. Discount Factor = 1 / (1 + YTM)^Year
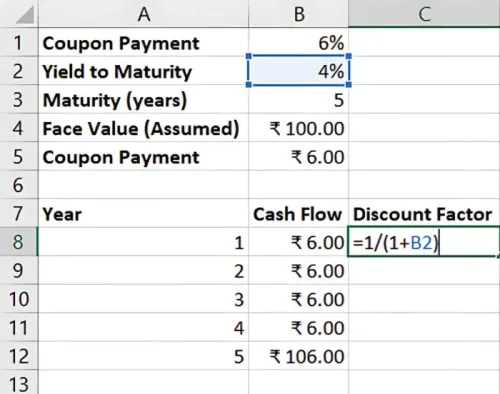
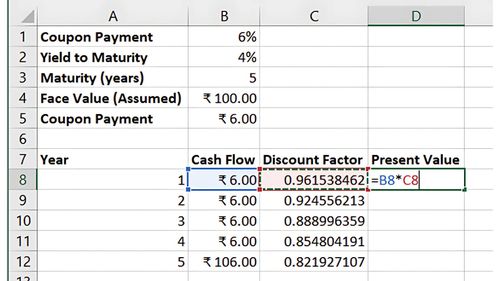
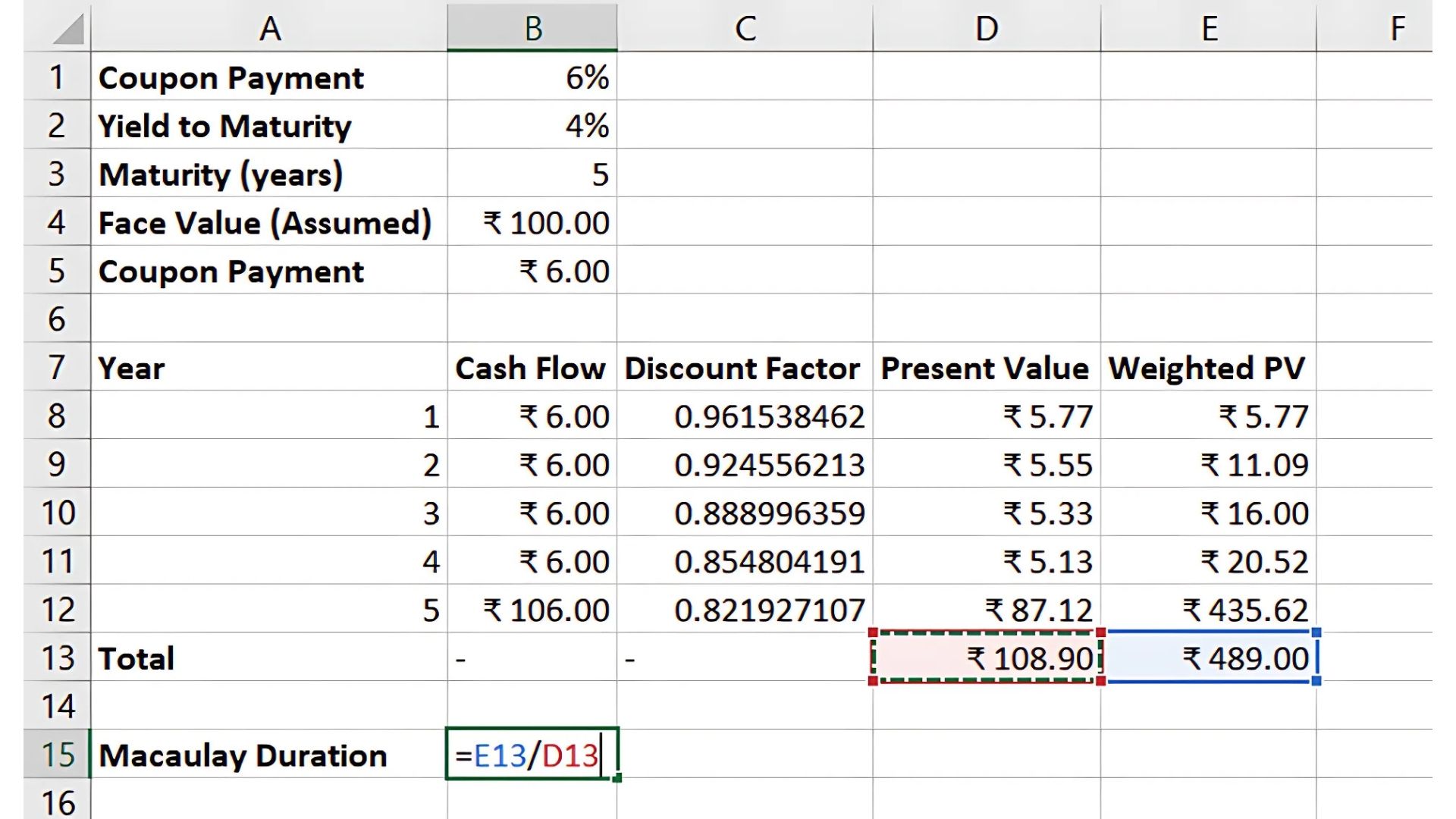
Step 2: Calculate Macaulay Duration
In Excel, Macaulay Duration can be calculated by weighting each period by its present value and summing these weighted periods.
Macaulay's Duration = Total Weighted PV / Total PV of Cash Flows
Weighted PV = Year × PV
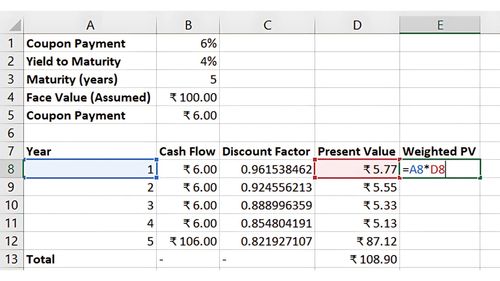
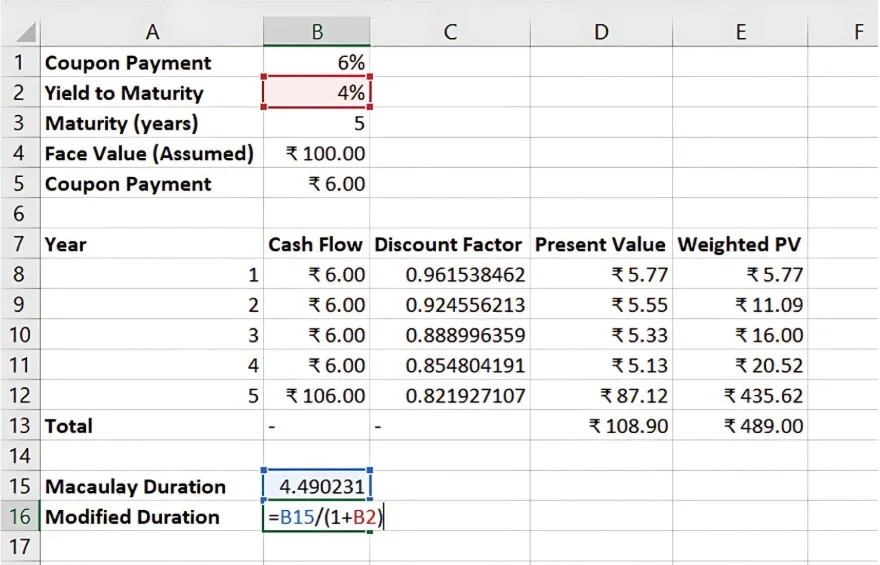
Step 3: Calculate Modified Duration
Using Macaulay Duration, apply the Modified Duration formula to calculate interest rate sensitivity.
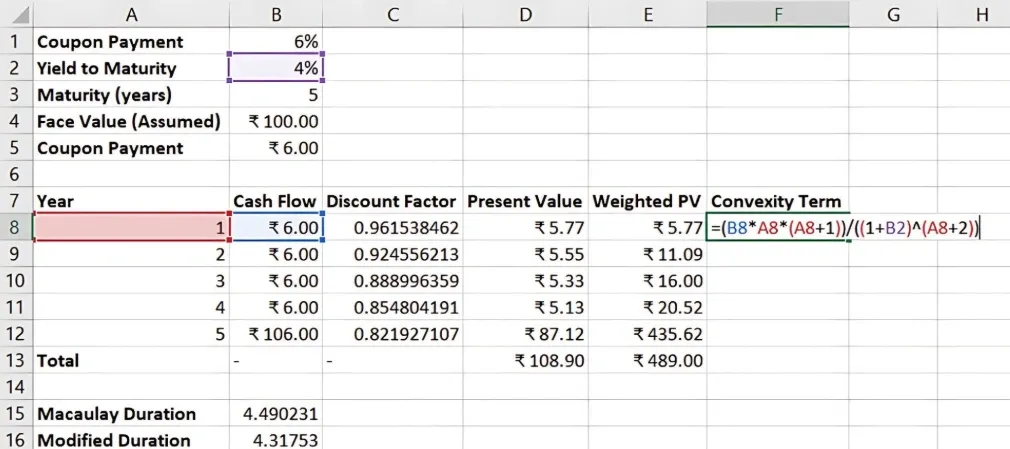
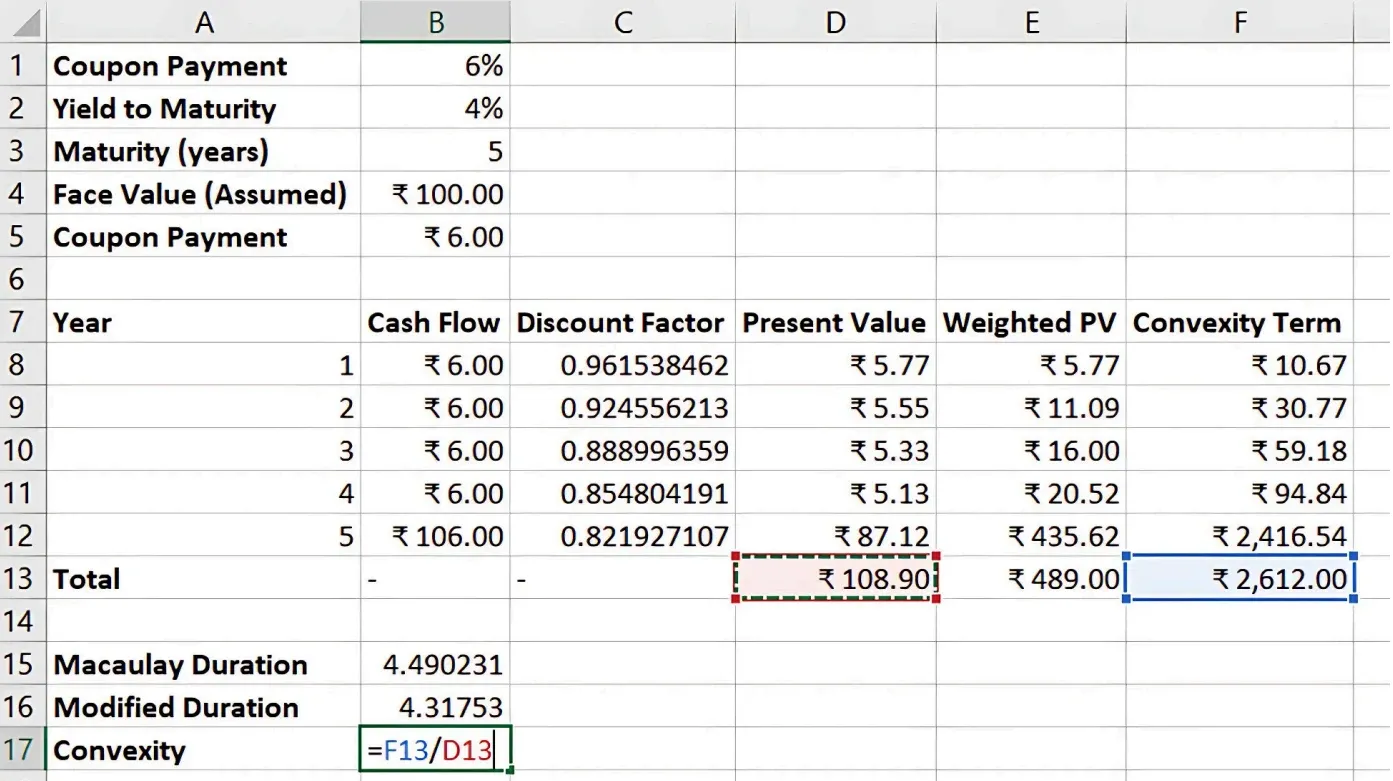
Convexity Calculation
Convexity measures the degree of curvature in the price-yield relationship, capturing how the duration changes as interest rates change.
Convexity Formula: Convexity = (1 / Price) × ∑ [Cash Flow × t × (t + 1) / (1 + Yield)^(t + 2)]
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Convexity in Excel
- Calculate the present value of each cash flow.
- Apply the convexity formula in Excel by summing the weighted cash flows.
Benefits of Using Duration and Convexity in Excel
-
Risk Management: Assess and manage bond portfolio exposure to interest rate changes.
-
Precision: Use convexity to adjust for inaccuracies in duration, especially for larger rate shifts .
-
Portfolio Optimisation: Compare bonds based on interest rate risk to select optimal investments.
Key Takeaways:
-
Duration provides a basic measure of price sensitivity to interest rate changes.
-
Convexity refines this measure by accounting for curvature, offering greater accuracy.
-
Excel streamlines these calculations, enabling comprehensive interest rate risk analysis.
Conclusion
Calculating duration and convexity in Excel provides a thorough understanding of bond price sensitivity, aiding in effective risk management. These metrics are invaluable for building resilient bond portfolios.
Next Chapter Preview: In the next chapter, we’ll discuss Bond Valuation: Premium, Par, and Discount Bond Calculations. This involves understanding bond pricing based on coupon rates and current interest rates, helping you assess whether a bond trades at a premium, par, or discount. Stay tuned!
Recommended Courses for you
Beyond Stockshaala
Discover our extensive knowledge center
Learn, Invest, and Grow with Kotak Videos
Explore our comprehensive video library that blends expert market insights with Kotak's innovative financial solutions to support your goals.














