

Kotak
Stockshaala
Chapter 1 | 2 min read
Bond Price Calculation Using Excel
Understanding bond pricing is essential for assessing the value of fixed-income investments. Bonds are typically priced based on the present value of their future cash flows, which consist of periodic coupon payments and the face value at maturity. Using Excel, you can easily calculate bond prices, accounting for factors like the bond’s coupon rate, yield to maturity (YTM), and remaining time to maturity.
Why Calculate Bond Prices?
- Valuation: Determine if a bond is priced fairly in the market.
- Investment Decisions: Compare bonds with different maturities, coupons, and yields.
- Yield Analysis: Analyse the yield required by the market based on a bond’s price.
Key Components of Bond Pricing
- Coupon Payments: Periodic interest payments based on the bond’s coupon rate.
- Face Value: The amount paid back to the bondholder at maturity.
- Discount Rate: The required rate of return or yield to maturity (YTM).
Formula for Bond Price Calculation
A bond’s price is the sum of the present values of its future cash flows. The formula is:
Bond Price = ∑ [Coupon Payment / (1 + YTM)^t] + [Face Value / (1 + YTM)^n]
Where:
- Coupon Payment = (Coupon Rate × Face Value) / Number of Payments per Year
- t = Each period up to the maturity date
- n= Total number of periods to maturity
Step-by-Step Guide for Bond Price Calculation in Excel
Step 1: Define Bond Parameters
Let’s say you have a bond with the following characteristics:
- Face Value = ₹1,000
- Coupon Rate = 5%
- YTM = 6%
- Maturity = 10 years
- Annual Coupon Payments
Face Value | ₹1,000 |
Coupon Rate | 5% |
Yield to Maturity (YTM) | 6% |
Maturity (Years) | 10 |
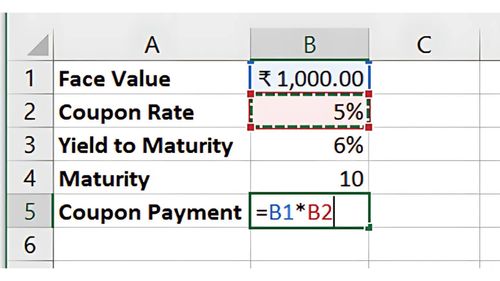
Step 2: Calculate the Coupon Payment
The annual coupon payment is:
=Face Value * Coupon Rate
In this case:
=1000 * 5% = ₹50
Step 3: Apply the Bond Pricing Formula
In Excel, you can calculate the bond price using the PV function to find the present value of the cash flows:
=PV(YTM, Maturity, -Coupon Payment, -Face Value)
For this example:
=PV(6%, 10, -50, -1000)
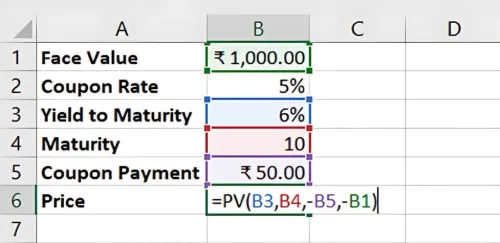
Result: The bond price is approximately ₹926.39, meaning the bond trades at a discount to its face value, as the YTM is above the coupon rate.
Benefits of Using Excel for Bond Pricing
- Automation: Calculate bond prices easily for different YTMs and maturities.
- Quick Comparisons: Evaluate bond prices with varying coupon rates or yields.
- Scenario Analysis: Test how changes in YTM impact the bond’s price.
Key Takeaways:
- Bond prices reflect the present value of future cash flows.
- Excel’s PV function simplifies bond pricing by automating calculations.
- Use bond pricing to make informed decisions and compare bond investments.
Conclusion
Excel provides a straightforward method for calculating bond prices, allowing investors to assess whether bonds are priced fairly or at a discount/premium.
Next Chapter Preview:
In the next chapter, we’ll cover Calculating Bond Yield to Maturity (YTM) and Yield to Call (YTC). These metrics help investors understand the potential returns on bonds held until maturity or call date. Stay tuned!
Recommended Courses for you
Beyond Stockshaala
Discover our extensive knowledge center
Learn, Invest, and Grow with Kotak Videos
Explore our comprehensive video library that blends expert market insights with Kotak's innovative financial solutions to support your goals.














