

Kotak
Stockshaala
Chapter 4 | 3 min read
Ratio Spread Strategy
Previously on Collar strategy, we've discussed what a conservative Collar may aim at: how to Lock in some profit on one end and hedge in some sort of downside on the risk side. Going forward in the series on Volatility Trading, let's transition up to the more intermediate advanced concept called the Ratio Spread strategy. This could give huge possible outcomes all across much more controlled positions. Again an optimum strategy for India's developed trader. This talks about how a ratio strategy actually functions in specific cases where that might play best.
What is a ratio spread strategy?
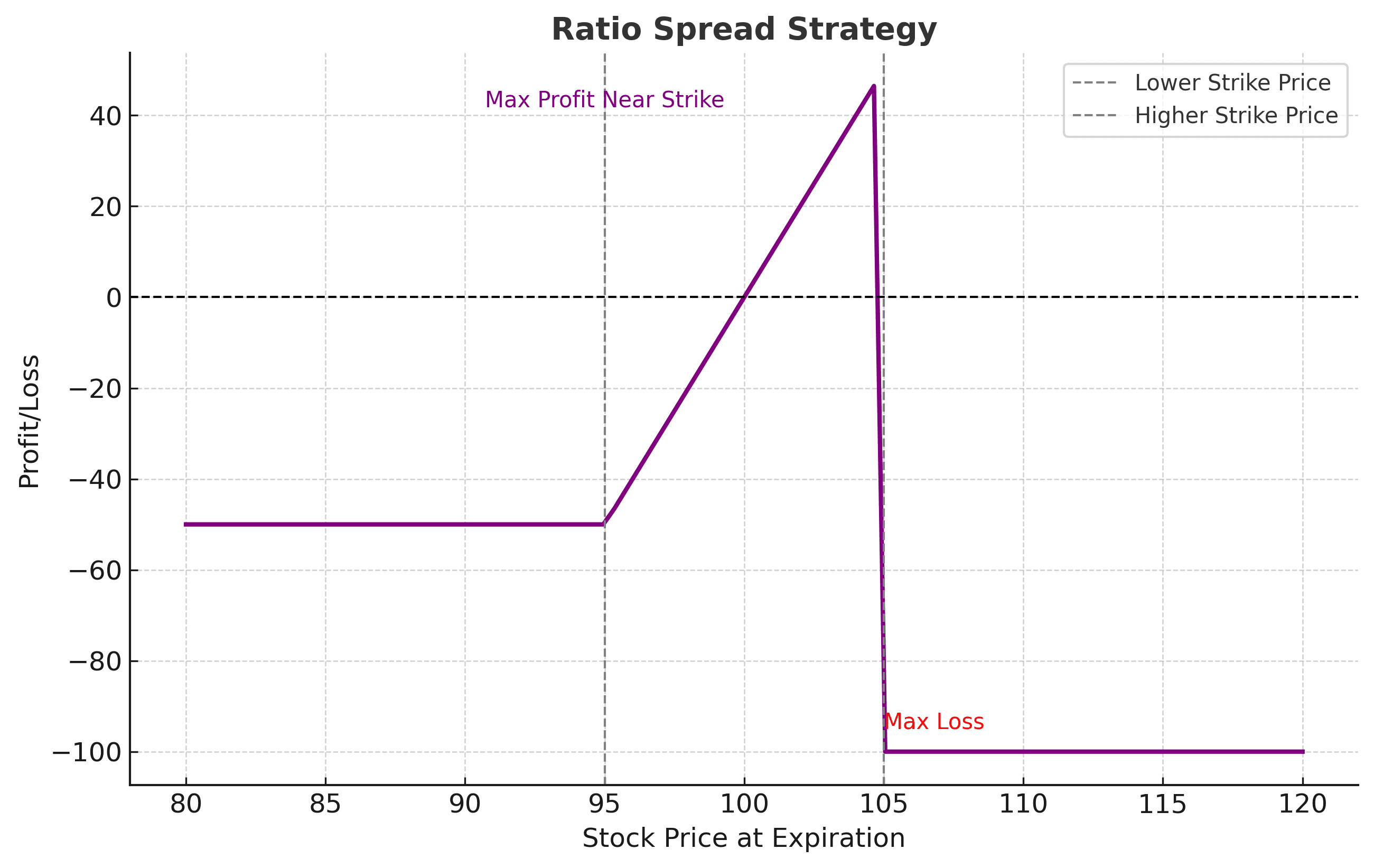
The Ratio Spread strategy presupposes buying one option (Call or Put) and selling multiple options of the same type but at different strike prices. Typically, the ratio is 1:2, where:
1. You buy one option with a lower strike price.
2. You sell two options at the higher strike price.
This is a net credit setup or small net debit, which gives you almost the right balance of risk as compared to reward. It works exceedingly well when one is projecting that the market is simply going to move moderately, either up or down in a certain direction.
For instance,
- A Call Ratio Spread is used in bullish markets.
- A Put Ratio Spread is used in bearish markets.
Why Traders Love It
Hence, when the Ratio Spread strategy is considered, it is pretty workable in India's vibrant market with indices like Nifty and Bank Nifty. Both of these provide very commendable liquidity and very frequent cases when a strategic trade can be done. Here's why Indian traders favor it:
1. Higher return potential: This strategy generates profit from moderate price movements.
2. Lower Capital Requirements: The cost of net credit or a small debit is relatively economical.
3. Defined Risk: While the risk is capped on one side, it is equally important to handle the uncovered leg with care.
When to Use the Ratio Spread?
The Ratio Spread is applied in the following situations:
1. Directional View: One would be using a Call Ratio Spread in case he expects a moderate upward move or would use a Put Ratio Spread for a moderate downward move.
2. Range-Bound Markets: This is when markets are in consolidation and might see limited directional movement.
3. Low Volatility: Works well when volatility is low because the premium for sold options would be greater.
How to Set It Up: An Example
Call Ratio Spread Example (Bullish View)
Suppose Nifty is trading at 19,600 and you expect it to go up reasonably but not cross 19,900.
- Buy 1 Nifty 19,600 Call at ₹ 100.
- Sell 2 Nifty 19,900 Calls at ₹ 50 each.
Net Credit: ₹ 50 (₹ 100 paid - ₹ 100 received).
Maximum Profit: If the Nifty expires close to 19,900, then you will receive a net premium plus intrinsic value.
Risk: In case Nifty shoots up drastically above 19,900, loss may be incurred on account of an uncovered leg.
Ratio Spread Example Bearish View
If you expect Nifty to fall moderately:
- Buy 1 Nifty 19,600 Put for ₹ 120.
- Sell 2 Nifty 19,300 Puts for ₹ 70 each.
Net Credit: ₹20 (₹120 paid - ₹140 received).
Maximum Profit: If Nifty closes at around 19,300 at expiry.
Risk: If Nifty falls sharply below 19,300.
Key Benefits
1. Cost-Effective: In this way, the initial cost becomes offset by net credit and is thus quite attractive for low capital traders.
2. Profit Potential: Provides a very good return in case of a moderate move in the market in the expected direction.
3. Versatility: Can be applied to both bearish and bullish markets.
Risks to Watch
While the Ratio Spread offers controlled risk on one side, the uncovered leg introduces unlimited risk in case the underlying moves beyond the higher strike price in Call Ratio Spreads or lower strike price in Put Ratio Spreads sharply. It is one of those spreads that calls for caution and monitoring.
Conclusion
The ratio spread strategy will be a strong strategy for traders who wish to gain from moderate price movements, not with very heavy upfront costs. This requires great understanding of the market's behavior and a good risk management system. Hence, it would be ideal for experienced traders. If you found this strategy fascinating, make sure to check out our next chapter on Synthetic Positions, where advanced strategies replicate actual stock positions using options for creative ways to manage risk and efficiently use capital.
Recommended Courses for you
Beyond Stockshaala
Discover our extensive knowledge center
Learn, Invest, and Grow with Kotak Videos
Explore our comprehensive video library that blends expert market insights with Kotak's innovative financial solutions to support your goals.














